CRD #17
On ransomware payments, MITRE ATT&CK techniques, OT security, and DDoS targeting.

The Cybersecurity Research Digest cuts through the marketing fluff and bias to bring you relevant and objective insights on cybersecurity stats and trends, all backed by empirical data.
The post features highlights from trustworthy research sources released between February 2-17, 2025, followed by a list of all monitored reports.
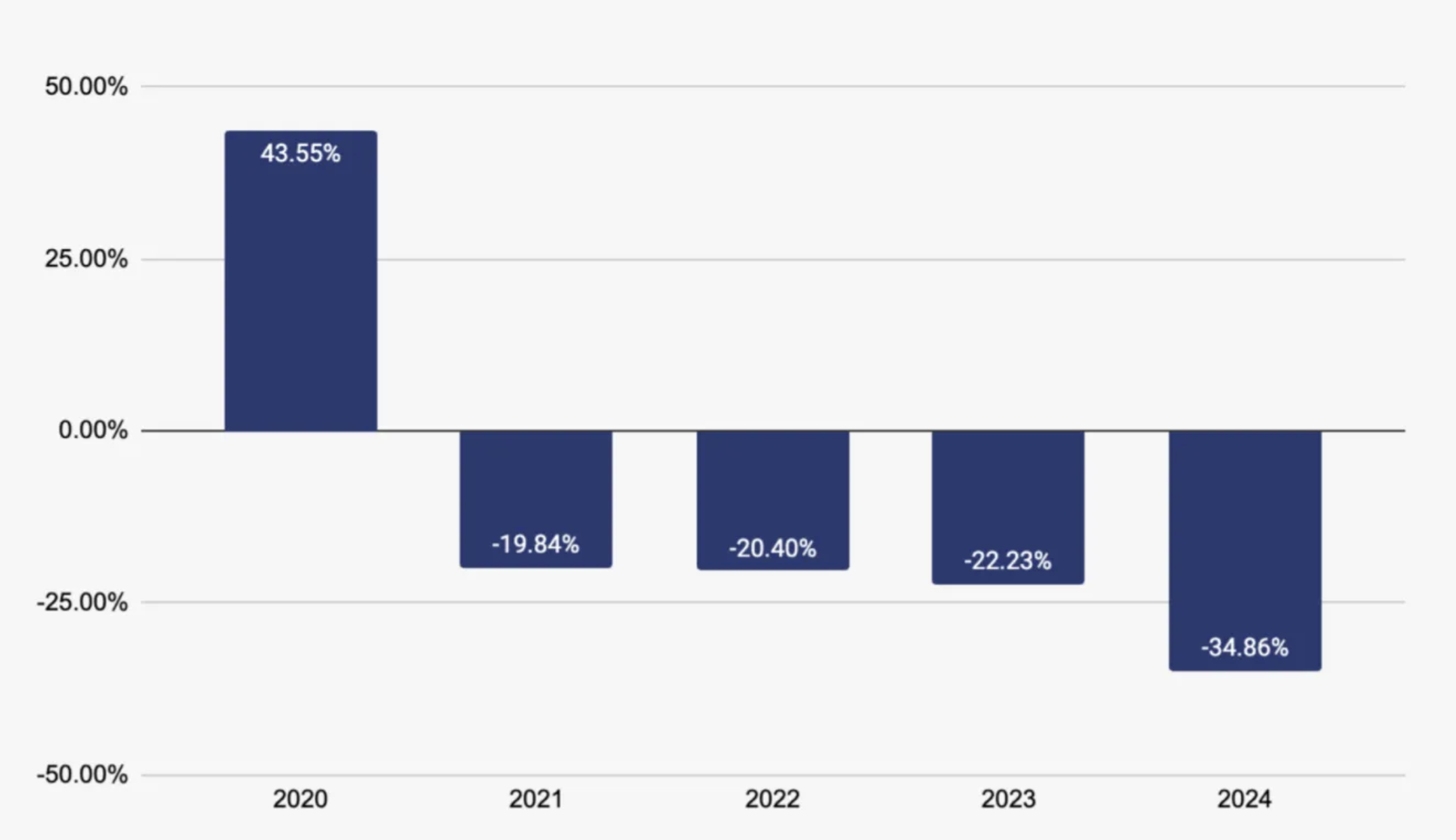
Positive signs from crypto transaction data: ransomware payments down

Analysis of cryptopayments shows a 35% year-over-year decline in total ransom payments in 2024.
The data shows that even though more ransomware events occurred in H2 2024 (measured by the number of victims listed on leak sites), fewer organizations – less than half – chose to pay.
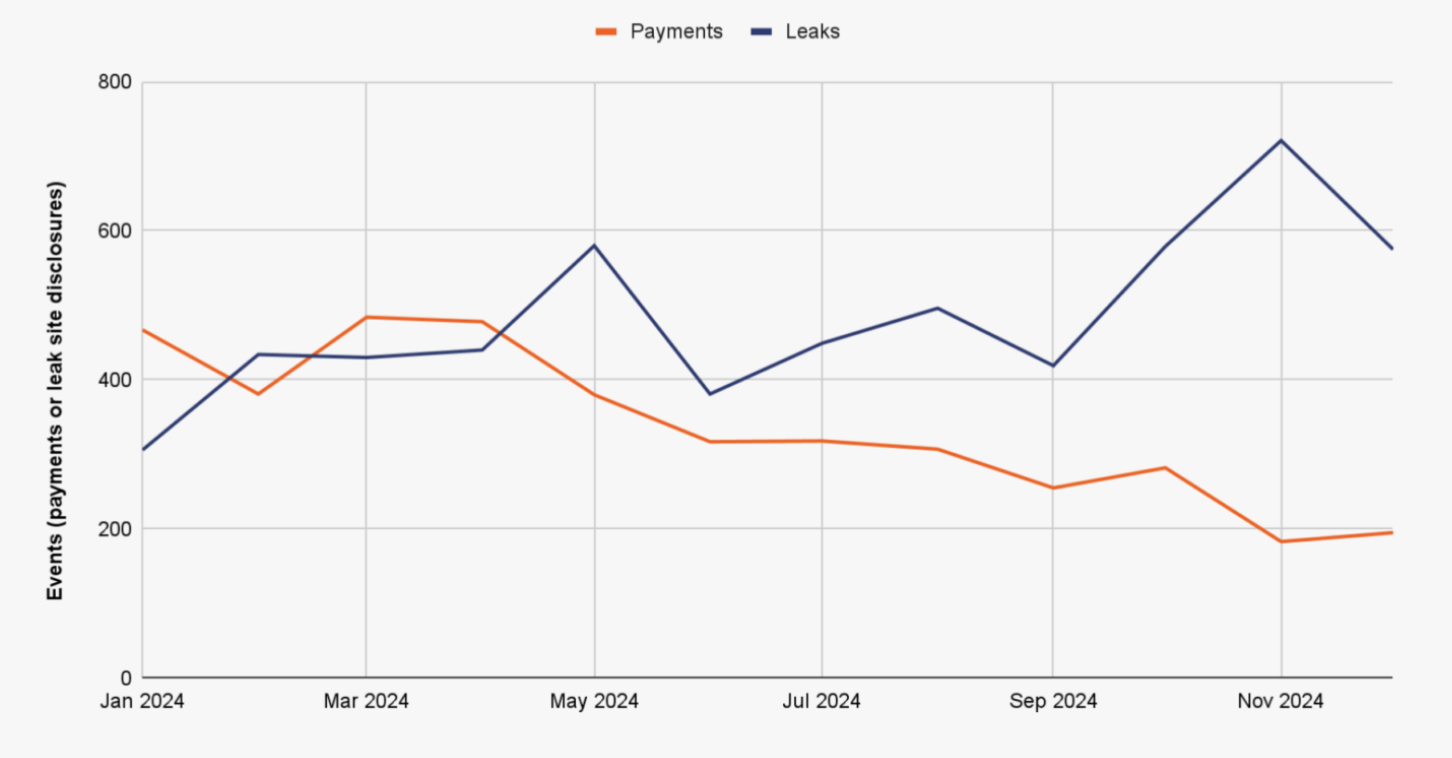
These positive trends likely result from a combination of factors, including the effectiveness of international law enforcement efforts, improved organizational preparedness — such as enhanced backup strategies — and a broader shift in victim responses, with an increasing willingness to resist ransom demands.
Furthermore, the data from 2024 reveals that ransomware actors operated within three distinct tiers based on payment demands. Lower-tier groups typically received payments below $1,000, while a mid-tier cluster targeted victims with ransom demands around $10,000. At the highest level, more sophisticated actors demanded payments exceeding $100,000, with some cases surpassing $1 million. The data also indicates a growing prevalence of high-value ransom events, suggesting an increasing proportion of attacks involving demands above $1 million.
MITRE ATT&CK insights: top 12 techniques drive 93% of actions
An analysis of over one million malware samples collected between January and December 2024 revealed that 93% of malicious actions in 2024 leveraged the top ten MITRE ATT&CK techniques. This finding clearly reinforces the need for security teams to prioritize defenses against the most prevalent threats.
The analysis also showed a threefold surge in malware targeting credential stores, rising from 8% in 2023 to 25% in 2024, underscoring the increasing effectiveness and preference for credential theft among threat actors.
Other key findings included:
- Modern malware continues to exhibit increasing sophistication, executing an average of 14 malicious actions and utilizing 12 ATT&CK techniques per sample.
- Stealth techniques remain central to attacker strategies, with Process Injection (T1055) observed in 31% of samples, enabling malicious code to evade detection within legitimate processes.
- The exploitation of native scripting tools, particularly Command and Scripting Interpreter (T1059), remains widespread, allowing attackers to leverage PowerShell and Bash.
- Credential theft continues to drive lateral movement, with Credentials from Password Stores (T1555) appearing in 25% of malware samples as sttackers increasingly target password managers and cached login data to gain elevated access.
Old CVEs dominate OT security incidents
Research based on telemetry from Palo Alto Networks' OT security products shows that manufacturing remains the most targeted and compromised industry, accounting for nearly 90% of network-internal exploit attempts observed by the company.
The continued reliance on legacy systems in OT networks is a key enabler of these exploitations, with the research showing that over 60% of exploit triggers were linked to CVEs at least six years old.
The most prevalent exploitation method involved the use of remote services for initial access, representing 20% of observed incidents. Additionally, nearly 80% of malware detected by the company was classified as "unknown," suggesting that threat actors are consistently deploying novel variants.
DDoS attacks: gaming and financial services top targets
A global cloud service provider’s report confirms that gaming remains the most targeted industry for DDoS attacks, accounting for over one-third of incidents. Service disruptions are frequently used to manipulate online tournaments, while downtime directly impacts revenue, making gaming a prime target for ransomware actors increasingly using double or triple extortion tactics.
The report also highlights a surge in attacks on financial services, now comprising a quarter of incidents. Like gaming, the sector is highly sensitive to availability issues, making it attractive for disruption-based extortion schemes.
Reports monitored: 4-17 February
To take a deeper dive in the topics most relevant for you, find below a list of all the monitored research reports (31) that were published during the observed period.
About
evisec's Cybersecurity Research Digest provides security leaders verified strategic insights via a carefully curated weekly summary of evidence-led, unbiased and objective cybersecurity research publications. Read more about our service here.
✉️ Suggestions or want to collaborate? Get in touch via LinkedIn or email (henry@evisec.xyz)




