CRD #19
On ransomware stats, vulnerability exploitation, identity compromise and disruptive tactics.

The Cybersecurity Research Digest cuts through the marketing fluff and bias to bring you relevant and objective insights on cybersecurity stats and trends, all backed by empirical data.
The post features highlights from trustworthy research sources released between March 4-24, 2025, followed by a list of all monitored reports.
February 2025 saw more ransomware victims than ever
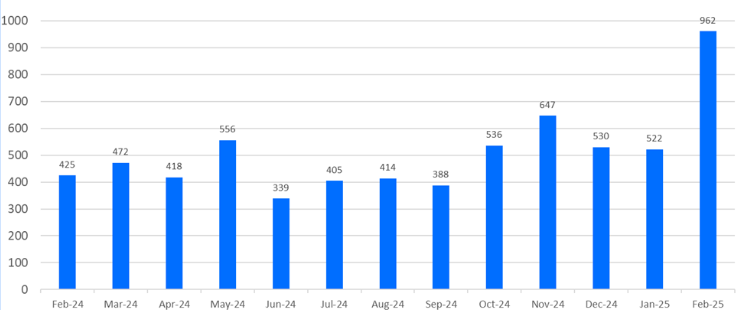
While ransomware activity month-over-month has remained relatively stable over the past year (monthly average of 417), February 2025 saw a significant surge according to leak site data. The victim count reached 962 in February 2025. This is more than double the monthly average and marks the highest monthly total on record.
Approximately one-third of these incidents were attributed to the Cl0p ransomware group. The fact that most attacks are carried out by a few groups shows that related cyber threat intelligence (CTI) to track the TTPs of these prominent actors can be effective.
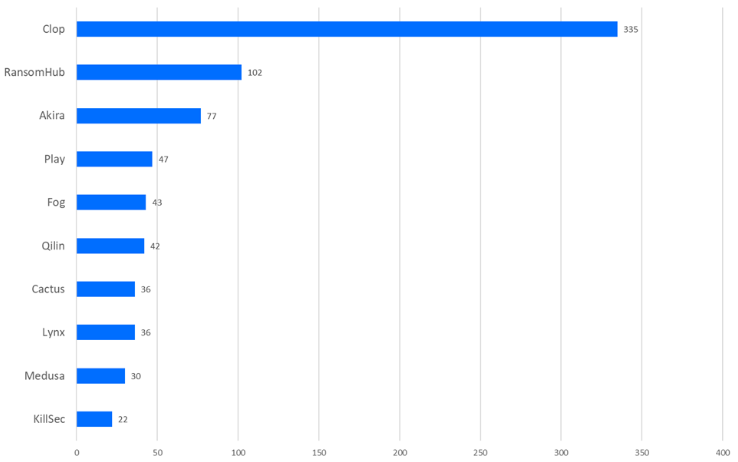
Some observers attribute this spike to ransomware groups shifting away from highly targeted attacks toward exploiting vulnerabilities at scale. Attackers increasingly use automated scanning techniques, targeting newly disclosed vulnerabilities in edge devices immediately following public disclosure. This allows for fast and efficient abuse of readily available proof-of-concept exploits that facilitate remote control. However, as this approach is not new, it does not fully explain the major spike in reported incidents in February 2025. If this heightened level of activity continues, further analysis will be necessary to understand whether this represents a more fundamental shift in threat actor strategies and efficiency.
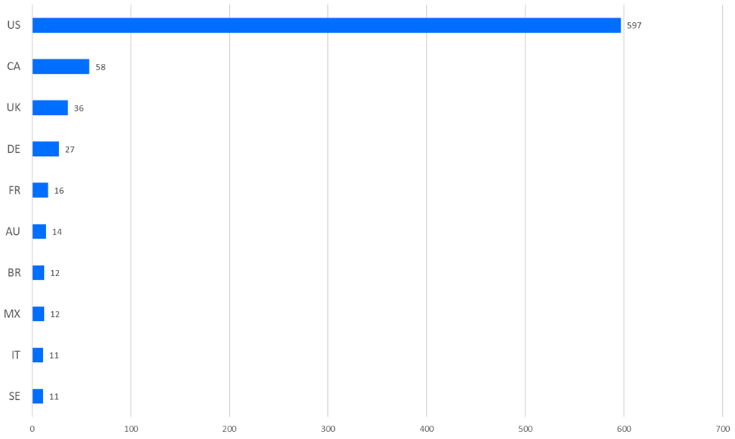
Furthermore, leak site data continues to show that the United States remains by far the most heavily targeted country for ransomware attacks (at least according to primarily Western CTI providers).
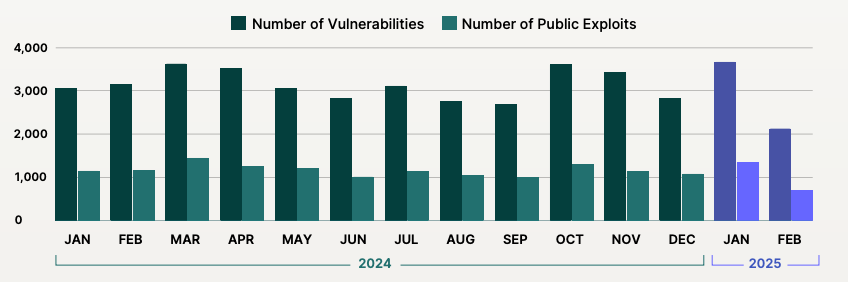
At the same time, published vulnerabilities continue to steadily increase, posing ongoing challenges for Vulnerability Management teams. In 2024 alone, over 37,000 vulnerabilities were disclosed, a 12% increase from the previous year.
The continuous surge, amplified by regular Patch Tuesday updates and an expanding number of CVE advisories, means that addressing every vulnerability individually is impractical. Organizations thus need to adopt a risk-based approach to patch prioritization
Identity compromise dominates incident response engagements
Compromised credentials remain the most prevalent initial access vector in serious cybersecurity incidents, consistently highlighted across multiple threat reports analyzing 2024 threat and incident response data.
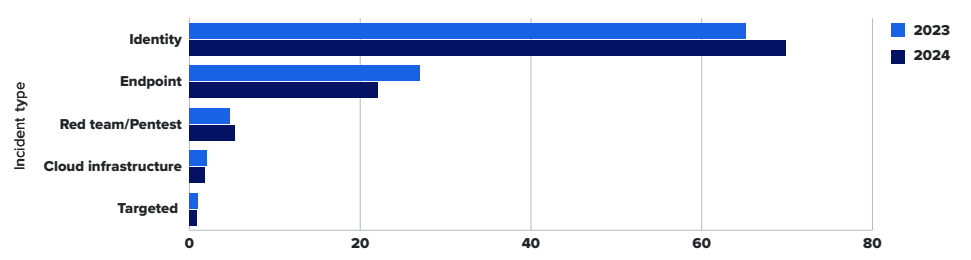
Insurance claims data from 2024 indicates that nearly half (47%) of ransomware cases involved compromised credentials, typically targeting Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) and VPN services. This is further supported by data from an MDR provider, showing that identity-related cases accounted for nearly 70% of all incidents in 2024.
Social engineering attacks—now more sophisticated due to Generative AI—continue to play a central role in credential theft. However, data also shows that organizations frequently fail to implement basic security measures effectively as brute-force attacks remain highly successful, contributing to 42% of identity-compromise cases in insurance claims. This aligns with findings from incident response teams, which identified weak passwords and absent multi-factor authentication (MFA) as root issues.
Additionally, infostealers have emerged as the dominant malware type deployed in endpoint incidents. The initial access marketplace continues to expand significantly, with 3.2 billion compromised credentials available in 2024—a 33% increase from the previous year—of which infostealers were responsible for approximately 75%.
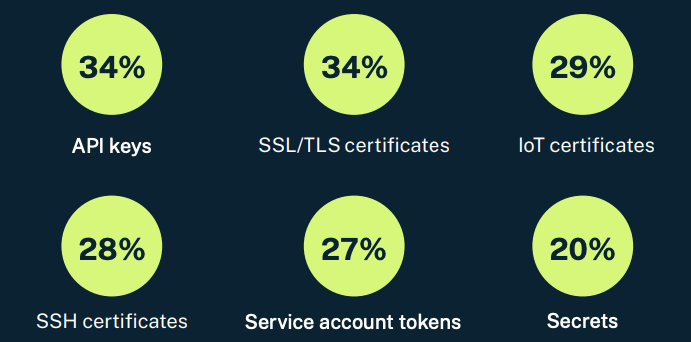
The extensive and growing reliance on machine identities further complicates these risks. A survey of 1,200 security leaders indicated that half experienced significant breaches directly linked to compromised machine identities, primarily involving API keys and SSL/TLS certificates. With machine identity usage expected to increase by up to 150% within the next year, securely managing these identities has become critically important.
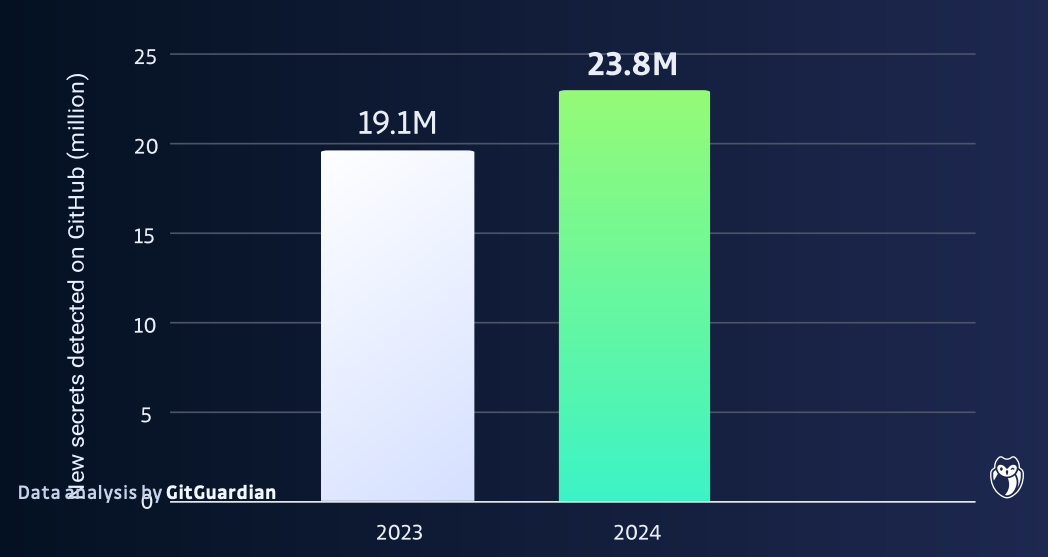
Credential leaks frequently occur even without targeted attacks. Analysis from GitGuardian revealed over 23 million hardcoded secrets publicly exposed on GitHub in 2024—a 25% year-over-year increase, despite GitHub’s preventive measures during code pushes. Notably, repositories utilizing GitHub Copilot experienced a 40% higher incidence of leaked secrets, confirming the security concerns commonly associated with using Large Language Models (LLMs) for code generation.
Importance of resilience capabilities as threat actors seek disruption
Incident response data from 2024 underscores a growing emphasis by threat actors on causing intentional operational disruption. Financially motivated attackers have increasingly shifted their strategies toward deliberate sabotage—destroying systems, restricting access to critical resources, and causing extended downtime—to maximize pressure on victims and compel ransom payments. According to Unit 42, 86% of incidents in 2024 resulted in measurable business impacts, including:
- Complete operational disruption
- Asset loss and fraud
- Reputational and market damage resulting from publicly disclosed attacks
- Increased operational, legal, and regulatory costs
The ongoing creativity of threat actors in identifying new pressure points highlights the critical importance of developing comprehensive resilience capabilities. This includes not only robust cyber resilience measures, such as effective backups and technical recovery processes, but also holistic organizational incident response plans incorporating operational, business continuity, and communication strategies.
Reports monitored: 4-24 March
To take a deeper dive in the topics most relevant for you, find below a list of all the monitored research reports (31) that were published during the observed period.
About
evisec's Cybersecurity Research Digest provides security leaders verified strategic insights via a carefully curated weekly summary of evidence-led, unbiased and objective cybersecurity research publications. Read more about our service here.
✉️ Suggestions or want to collaborate? Get in touch via LinkedIn or email (henry@evisec.xyz)




