CRD #20
On UK's national cyber resilience, most leveraged attack vectors, insurance claim data, ransomware and social engineering trends.

The Cybersecurity Research Digest cuts through the marketing fluff and bias to bring you relevant and objective insights on cybersecurity stats and trends, all backed by empirical data.
This post features highlights from trustworthy research sources released between March 25 and April 14, 2025, followed by a list of all monitored reports.
TL;DR
- UK survey results suggests a relative equilibrium between defensive posture and adversary activity—national cybersecurity indicators year-over-year show no significant shifts, positive or negative.
- US insurance claim data for 2024, however, points to a rise in incidents and a return to 2021 ransomware levels, with remote access used as the entry point in 80% of cases.
- Global incident response data highlights a continued reliance on old and well-known vulnerabilities as well as compromised identities—an important reminder as a guide to develop defensive measures.
- Stolen identities also underpin the majority of phishing attempts, which now almost universally feature some form of AI-generated content.
UK Cyber Breach Survey: a national snapshot of cyber resilience, balancing vendor-led narratives
Surveying over 2,000 businesses, 1,000 UK-registered charities, and 500 educational institutions, the annual UK government-backed Cyber Security Breaches Survey offers a broad, non-commercial snapshot of national cyber resilience. Results for 2024 show no drastic changes compared to last years, though some metrics improved modestly.
Around four in ten businesses reported experiencing a cybersecurity breach or attack in the past year—a slight decrease from 50% in 2023. The decline was seen as primarily driven by fewer phishing incidents among micro and small businesses, possibly reflecting improved cyber awareness among smaller organisations. However, the proportion of medium (67%) and large businesses (74%) reporting incidents remained high and consistent with previous years.
Phishing remains the most common and disruptive breach type, affecting 85% of UK businesses. Among those affected by breaches, around one in six (16%) experienced a negative outcome, showing that most attacks were unsuccessful. Where attacks did succeed, the most commonly reported impacts were temporary loss of file or network access and website disruption—indicators largely unchanged from prior years.
The survey offers a clear counterpoint to industry benchmarks, contrasting for example IBM’s often-cited $4.8 million average breach cost with significantly lower self-reported figures. When excluding zero-cost incidents, the average cost of the most disruptive breach was £3,550 for businesses and £8,690 for charities. This disparity stems from differing methodologies and samples: IBM’s figures reflect large enterprises and comprehensive breach-related costs—including detection tools, legal fees, and business losses—while the UK survey captures direct, perceived impacts across a broader organisational spectrum. Nevertheless, consistent year-on-year methodology provides value for tracking trends, showing only modest increases since 2023.
The survey also assessed how cybersecurity is prioritized within organizations. While 72% of businesses still consider cybersecurity a high priority, board-level accountability has declined steadily—from 38% in 2021 to 27% in 2025. This again diverges from some vendor-led studies that claim growing CISO presence at the board level, underscoring how differences in sample composition influence such findings. Larger, regulated firms are naturally more likely to have formalized executive oversight of cybersecurity.
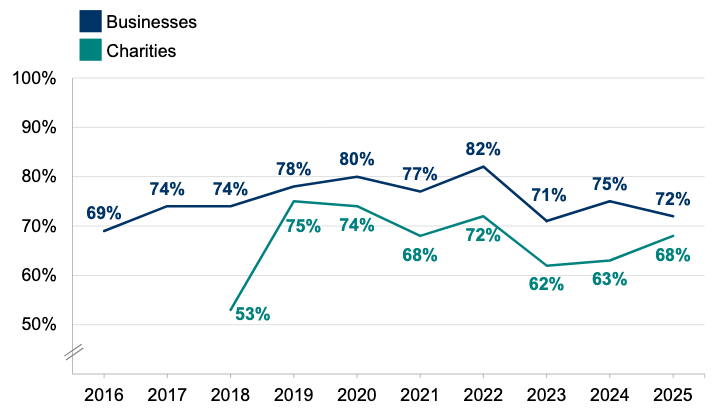
Finally, the study confirms a rising reliance on MSSPs and external providers, especially among small businesses—part of a broader shift toward outsourcing cybersecurity.
The importance of security fundamentals: patch known exploits and protect identities
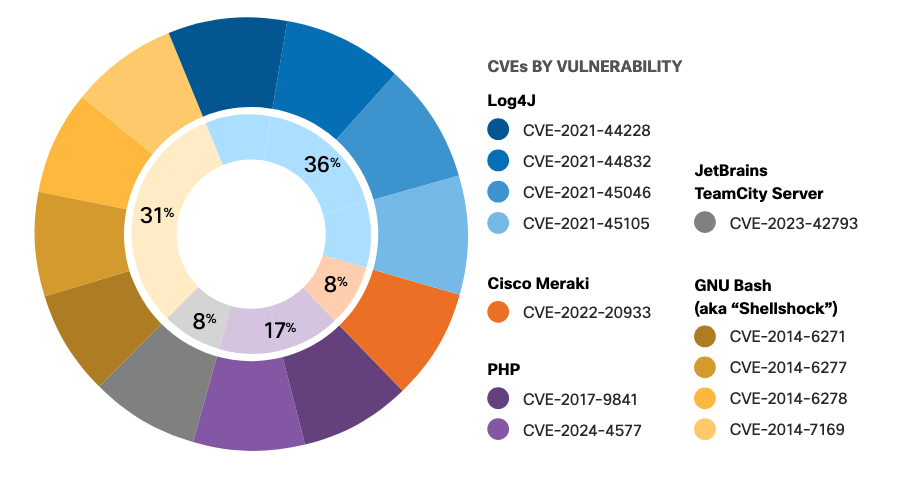
Global telemetry from over 46 million devices and incident response engagements by Cisco Talos highlight a simple fact: threat actors choose the path of least resistance to maximize outcomes. The top-targeted vulnerabilities in 2024 were mostly older CVEs that have been public for years. Notably, four of the top twelve were published over a decade ago, and the well-known Log4j vulnerabilities—disclosed in 2021—still features prominently, underscoring that risk-led patch management remains a persistent challenge.
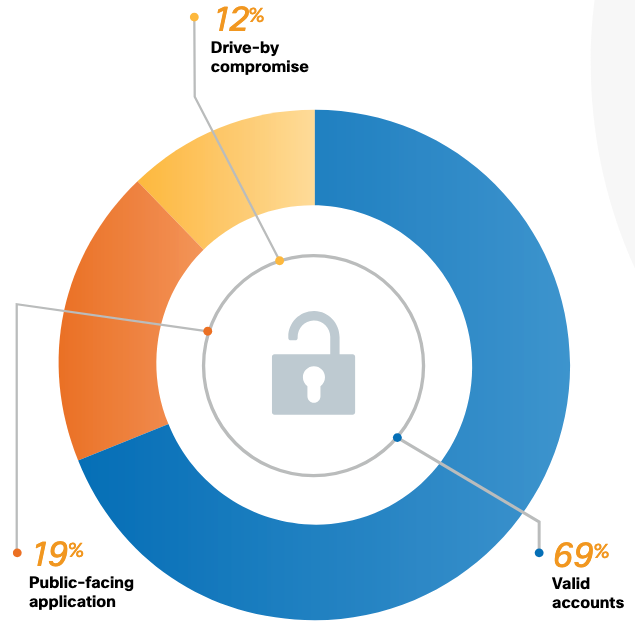
Incident response data further showed that leveraging legitimate assets continues to be the go-to method for threat actors, highlighting the need to prioritize identity protection and zero trust approaches as central pillars of defense strategies. Identity-related cases dominated IR engagements (accounting for 60%), with adversaries exploiting credentials, session tokens, API keys, and digital certificates across all phases of an intrusion—from initial access to lateral movement and privilege escalation. Once inside, attackers clearly favoured living-off-the-land binaries (LoLBins)—native tools such as PsExec, PowerShell, RDP already present on systems—over commercial or open-source tools.
The report also highlights that education, healthcare, and manufacturing remain among the most targeted sectors due to their combination of attractive characteristics: underfunded security teams, limited monitoring capabilities, poor device hygiene, minimal network segmentation, and the presence of valuable data or critical operations that can be leveraged for ransom.
Finally, while generative AI continues to be explored for social engineering, automation, and productivity tasks, the report finds that its feared impact on attacker TTPs has not yet materialized at scale, as no widespread or systemic use of GenAI to enhance offensive operations was observed.
Use of AI and compromised accounts dominate phishing attempts
Recent analysis of internal data from the past six months by a leading anti-phishing company highlights that stolen identities are heavily leveraged, with 57.9% of social engineering attacks originating from compromised accounts.
Regarding initial attack vectors, hyperlinks remain the preferred payload, accounting for 54.9% of phishing attempts. Malicious attachments were used in approximately 25% of cases, while about 20% relied purely on social engineering tactics (i.e., persuading victims to perform actions independently).
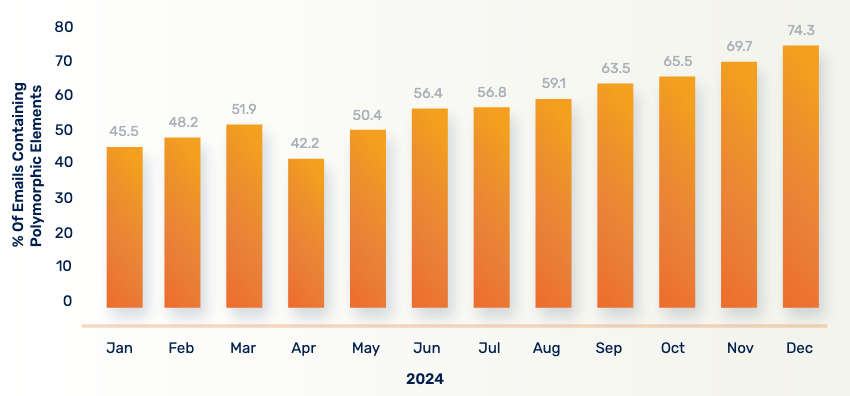
Of note, over 80% of phishing emails analyzed were classified as "utilizing AI," marking a substantial 53.5% year-over-year increase. Although the mere presence of AI in phishing attempts may not be actionable on its own—given AI’s growing ubiquity—the increasing sophistication and tailored nature of these attacks should inform related awareness and technical defense strategies. A clear indication of future trends is the rise in "polymorphic emails"—defined as a series of nearly identical emails differing only slightly—which increasingly bypass existing technical filtering solutions dependent on identifying previously known malicious content.
Additionally, the average phishing email length was 188 words, commonly incorporating terms such as "urgent," "review," and "sign." The most frequently leveraged sender platforms included DocuSign, PayPal, Salesforce, Microsoft, and Google—observations clearly indicating the persistence of established social engineering techniques designed to exploit trusted brands and instigate prompt responses from victims.
Financial fraud: the no. 1 cyber insurance claim in 2024
To balance the self-reported results from the UK, data from a US cyber insurer shows that cyber-related insurance claims rose 16% year-over-year in 2024, with financial fraud—primarily via business email compromise (BEC)—being the most common attack type. Correspondingly, email was the most frequent initial "attack vector" over all insurance cases.
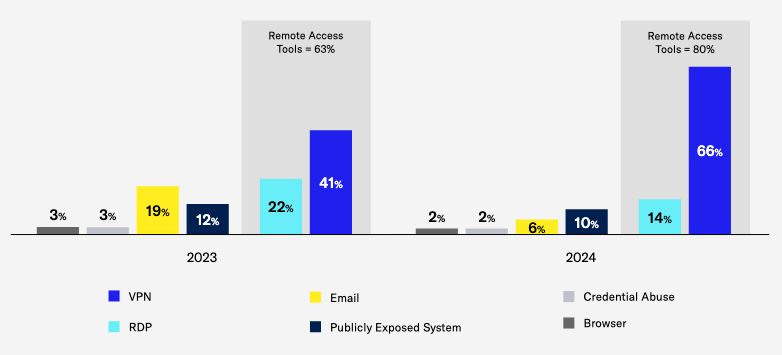
For cyber intrusions involving technical compromise rather than social engineering, ransomware claim frequency increased by 19%—returning to 2021 levels. The average severity of ransomware claims (representing the whole cost of the incident) rose as well by 13% to $468K, with remote access was the entry point in 80% of ransomware cases.
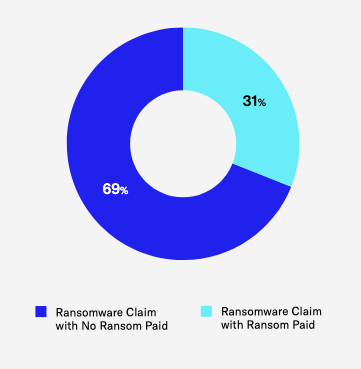
The average ransom paid also rose by ~12% to $317K, although payment occurred in just 31% of ransomware incidents—likely reflecting increased resilience capabilities among insured organizations, as well as a broader trend of resistance to demands.
Reports monitored: March 25 - April 14
To take a deeper dive in the topics most relevant for you, find below a list of all the monitored research reports (43) that were published during the observed period.
About
evisec's Cybersecurity Research Digest provides security leaders verified strategic insights via a carefully curated weekly summary of evidence-led, unbiased and objective cybersecurity research publications. Read more about our service here.
✉️ Suggestions or want to collaborate? Get in touch via LinkedIn or email (henry@evisec.xyz)




